How we speak
DESIGN DICTIONARY
Understand our design language and tools
#
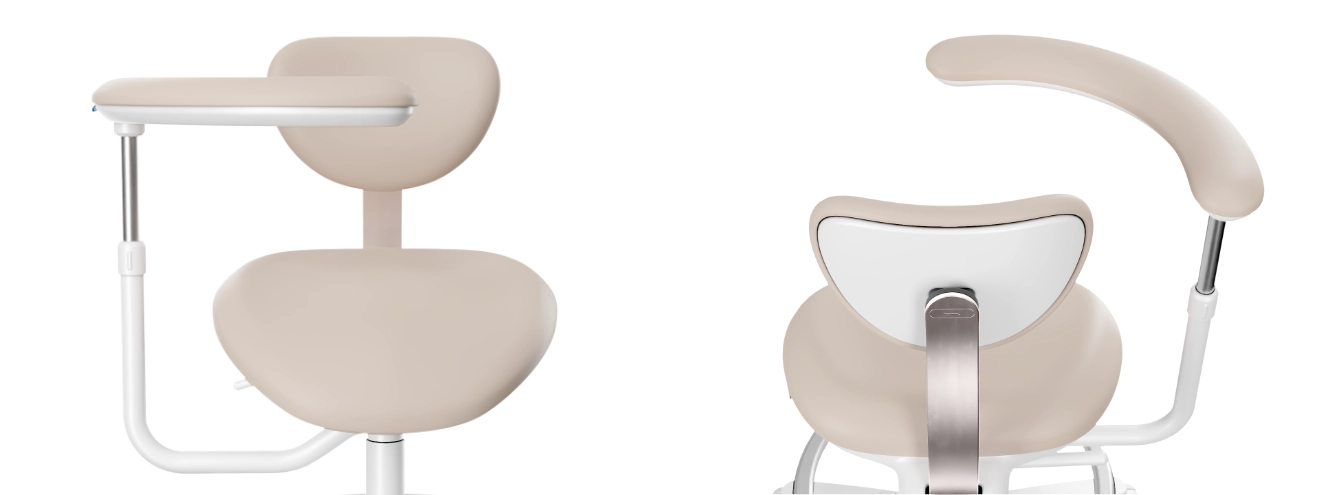
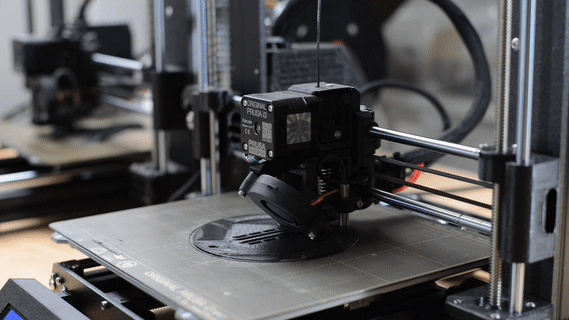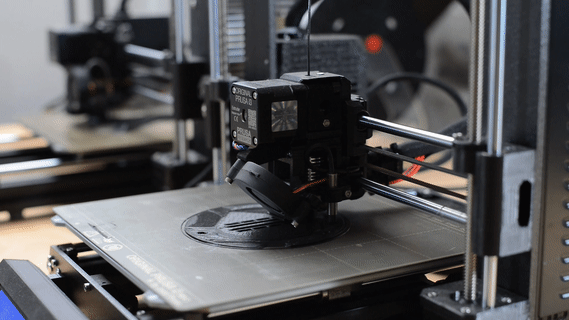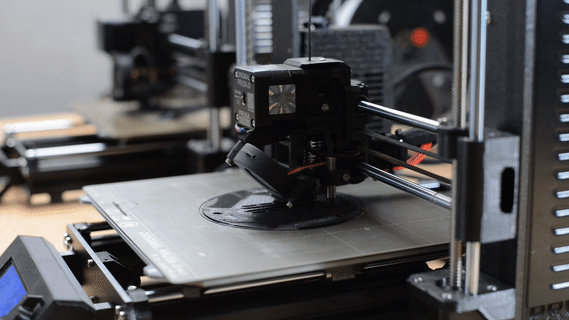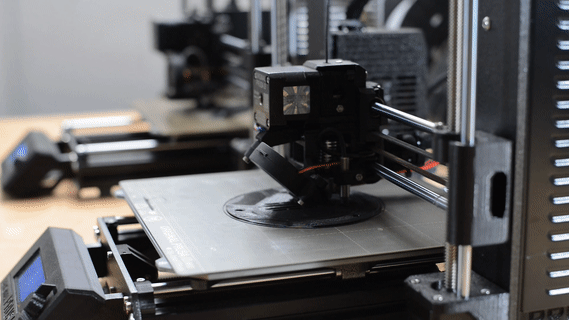
3D Print
3D printing is creating a physical object from a three-dimensional digital model, primarily by depositing many thin layers of material in succession.
We use this technique for fast and cost-effective prototyping, testing, or creating scale models.
(In the picture: 1:50 scale model of the Balaton boat).
A
ANIMATION
360° Rotation
The 360-degree rotation animation is a short digital video demonstration of a product, suitable for use on websites or in presentations.
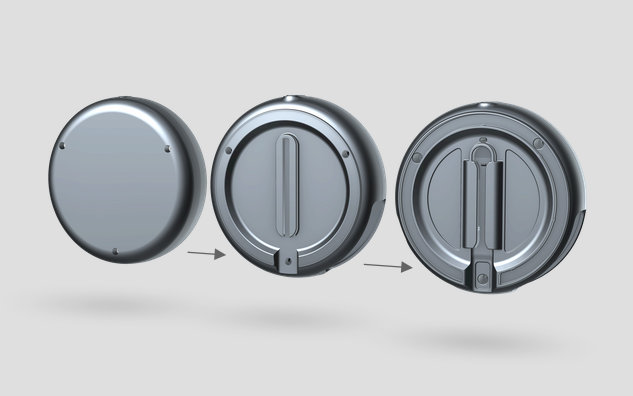
The displayed final product rotates 360 degrees around a specified axis against a neutral background. This type of animation can be played in an infinite loop with no visible edits. The animation can also include an exploded view that shows the individual parts of the product or, for example, a demonstration of configurations or color changes.
ANIMATION
Digital animation is an advanced digital video presentation of a product, suitable for placement on a website or in a presentation.
It is the digital replacement of a video presentation. The animation can include a pop-up view that shows the different parts of the product, or, for example, a demonstration of configurations, color changes, or other product features.
B
BODY FRAME
Superstructure and Chassis
A body frame, superstructure, or chassis is the physical frame or structure of an automobile, train, boat, airplane, or other multi-component device. This frame is designed by the engineering team (either from the client or by a third party).
C
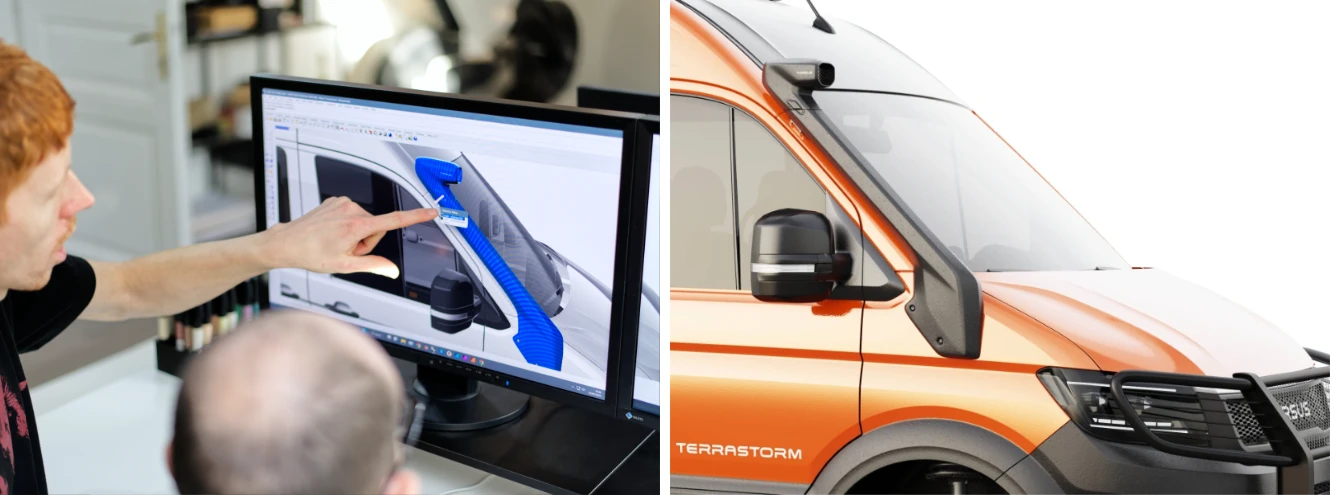
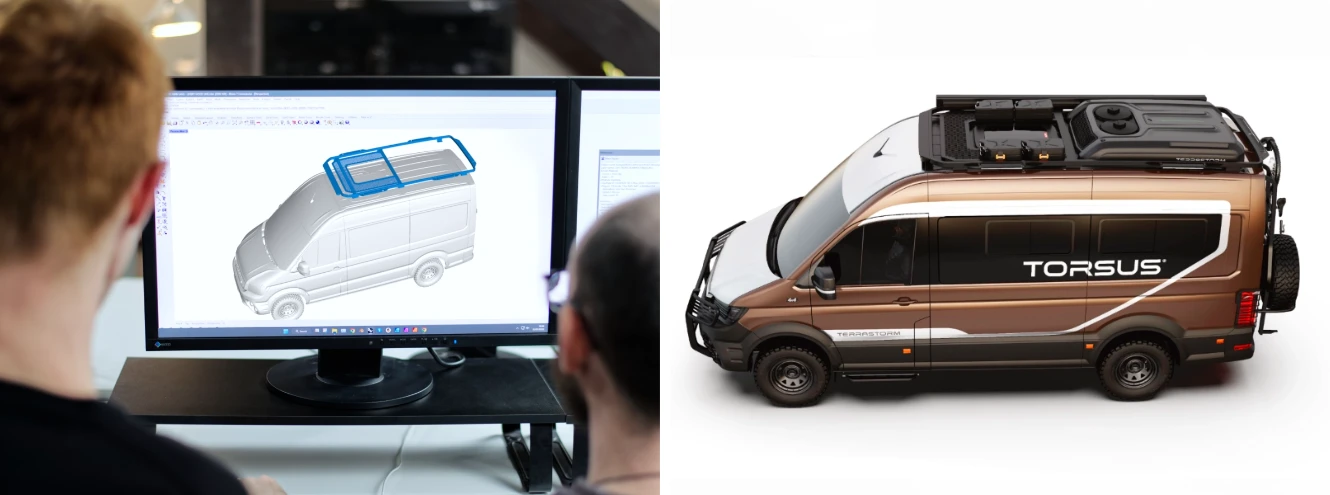
CAD / CAE / CAS
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) is the use of software for creating two-dimensional drawings (2D) but primarily for three-dimensional (3D) models. See the following terms: NURBS modeling and polygonal modeling. Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE) refers to tools used to analyze the robustness and performance of components and assemblies. Computer-Aided Styling (CAS) represents a 3D model of the external styling surfaces that the end user can see and touch.
CMF
Colors Materials Finish Design
Colors, Materials, and Finish Design is a design discipline where we select how the final surface of the product should look.
Concept design
Concept design or Concept phase is an early stage of the design process, aimed at creating key visual elements without the goal of producing documentation or materials for mass production.
Cost Optimization
Cost Optimization is a process throughout the entire design development, aimed at reducing development and manufacturing costs by selecting materials, choosing technology, reducing the number of molds, or limiting the number of suppliers needed.
D
Design concepts of access areas
And maintenance areas
Many of the products we design require access to hidden technical parts to function properly, for example, for maintenance or repair purposes. Such service openings also need a creative approach from the designer and can be designed by the product’s design language.
In addition to styling, great focus is placed on ergonomics and functionality.
Design Language
Design language, in terms of the design process, refers to creating a unique and recognizable visual styling for a product, which can and should be applied to the entire range of products from a single brand. This makes the product recognizable in the market and distinguishable from the competition.
Design Supervision
Overseeing the implementation of a design concept to ensure that the final product aligns with the original vision, functional requirements, and quality standards.
It bridges the gap between design and production by managing technical, aesthetic, and practical aspects throughout the project lifecycle.
We review prototypes, production processes, and materials to optimize the outcome.
Digital Presentation
And maintenance areas
For each project, we create 2 to 4 digital presentations that are easily shareable via common services (cloud, video meetings, e-mail). The presentation is usually in the form of a professionally designed PDF document and contains a complete description of the created design – from the explanation of the concept, through the presentation of the artwork development to the final photorealistic visualization.
Draft Angle
Draft angle is the angle of the side wall of each part designed to aid the removal of a part from mold. It is necessary to prepare 3D models of parts and moulds at the set draft angle. Each technology and supplier requires different draft angles. In general, draft angles from 1° – 5° are used. The most common technology requiring draft angle settings are injection moulding, thermoform vacuuming, and all types of molds for composites.
E
Exploded View
Exploded view could be a static image / video / digital animation video created in a rendering software, which shows the final product and its disassembly and reassembly into specific parts. Due to its length, it is suitable for use on web pages or in presentations and can be played in an infinite loop without visible cuts.
H
Hard Model
Scale model
Hard model is a scale model of the final design, which is made for the purpose of presentation and final validation of the design. It is produced by more advanced and precise methods to accurately represent the final product. These models are made of more durable materials such as plastic, wood, fiberglass or metal and usually have a surface treatment in the form of a polished lacquer or such material to match the real product.
L
Livery design
Livery design in terms of industrial and automotive design is mostly the design of the final outer surface of vehicle. It is most often done by wrapping vehicles with foil and other printed or non-printed stickers. It is a cost-effective way how to design various designs and strong identities of one vehicle. Livery design is usually used for racing cars or company-branded cars.
M
Mood Board
Moodboards are collages consisting of various objects that together form the visual style of the future design. Moodboards contain, for example, a colour scale, different textures, surfaces, inspiration sources and are wrapped together in a clear and unified format that is usually used as a stepping stone when building a design for a new product. Moodboard considers the client’s preferences and specifications but leaves a lot of freedom for the designer’s implementation.
N
Nurbs
Non-uniform rational basis spline (NURBS) is the most common type of 3D modelling based on very exact curves and surfaces. This type of 3D modelling is perfect for manufacturing purposes thanks to the very precise outcomes. But this technique is more time-consuming in comparison with polygonal 3D modeling. This is the reason why we are using this technique for 2nd stage of the design process. The mostly used file formats are .STEP and .IGS
O
OEM
Original equipment manufacturer (OEM) is an organization that makes devices from component parts bought from other organizations. We used this type of equipment for design projects, where is a high demand for a cost-effective solution. A great example of OEM parts is headlights for new vehicles. Instead of the very expensive development of new headlights, it is possible to use a standardized and already certified product from the OEM manufacturer.
P
Polygonal 3D model
A polygonal model is a type of 3D model great for the concept non-manufacturing stage of the design process. Compared to the Nurbs 3D model, the polygonal 3D model is a great way to convert ideas from paper to a 3D model as quickly as possible. Changes to the 3D model are less time-consuming. The 3D model can be used for the first initiation discussion with the engineering team to validate the design with technical parts, such as the frame / Superstructure / Chassis. The most used file formats are .OBJ or .FBX, after conversion, it could be non-manufacturing .STEP and .IGS file formats.
Press sketch
A press sketch is a final drawing of a product created primarily for marketing purposes to support a demonstration of the creative process of the product. Press sketch shows mostly the final product but in an artistic style of development sketch and is a kind of icing on the cake of every presentation materials. It also demonstrates the skill of the design studio.
Production surface
Surfaces in production quality are surfaces in their final stages for manufacturing purposes. After iterations in 3D polygonal modeling we Finish surfaces of all parts in Nurbs modeling with all manufacturing / suppliers technology requests (for example draft angles).
Proportion
Proportion is one of the fundamental elements of design. It refers to the relative size of the components of which an object is composed and their interplay and balance. The disproportion between the design elements can negatively affect the appearance but also the functioning of the product, so we devote a lot of effort to the correct proportions.
Prototype design
The Prototype Design phase involves creating functional models to test usability and delivering production documentation. Feedback and refinements ensure the design is production-ready, with all necessary data finalized for manufacturing and implementation.
Prototyping
Prototyping is an experimental process where a virtual idea is brought into tangible form of a physical model. Such a prototype can help to refine or validate a design concept in a real space and time. With the arrival of 3D printing, prototyping is simpler and faster than ever before and allows designers to create a large number of prototypes in a short time.
R
Revision / Iteration
Revision / Iteration is the repetition of a process in order to change design / technology / materials or any other updates during the design process. It could be requested from the client, supplier or any other unexpected element in the development process.
Rendering
Rendering is the process of generating an image from an empty 3D model using a graphics engine that adds scene, lighting, environments, materials, colors, shading, textures, and many other elements to the model that bring the resulting image closer to reality.
Research
Systematic research and study of materials and sources is an important part of the whole process of creating a new design. Research helps us to use the latest technologies and production materials, helps designers to follow and develop trends and avoid unwanted copying of existing designs. We use a lot of web tools to create a research, as well as catalogues, samplers, exhibitions, etc.
Reviewing Data
Collecting and checking different types of 2D and 3D data, specifications and documentation needed to create a basic project timeline. This is essential for optimal product development and smooth cooperation with the client.
S
Scale models
A scale model is a miniaturized physical representation of a virtual model that can be produced using a variety of techniques such as 3D printing, CNC milling or mould casting. Uses vary from simple models to control proportions and ergonomics to painted exhibition models with a high level of detail. The scale and range of materials used also varies.
Scope of work
The scope of work is a summary of all items, milestones, schedules, and outputs that each design contract contains and that must be created and completed in order for the final product to be successfully completed and delivered to the client.
Sketch Development
The first stage of design creation is done by sketching directly on the fundamental architecture of the designed product. Sketch development is happening in 2D space, either by the old-fashioned but still effective way of drawing with pencil on paper, or by more advanced tools such as digital drawing using professional graphic software.
Soft-Model
Type of scale model
A soft model is a form of a conceptual scale model of a product that is made from low-cost and more easily machined materials (e.g. polystyrene). This type of model is not used for final presentation, but for verification and validation of the design or ergonomics in space. It is possible to produce a large number of these models in a relatively short time to test different iterations and design variations.
Sustainability
Sustainable design seeks to reduce negative impacts on the environment. The basic objectives of sustainability are to reduce consumption of non-renewable resources, minimize waste, and create products that can help to keep healthy living environments.
V
Visualisation
The visualization is the result of rendering and post-processing that turns a simple 3D model into a photorealistic image in hi resolution. It is an important part of the design process and shows us exactly what the product will actually look like before it is actually physically produced. Visualization techniques have reached a level where it is often impossible to recognize a computer-generated image from reality.
VR
VR animation is a stereoscopic presentation of a product in the form of a digital video specially created for virtual reality display devices, such as VR headsets. Such animation creates a realistic three-dimensional experience of the product and may also allow the viewer to interact with the product or environment.
Let's make something great together
Get in touch with us to see how we can help you with your project